
JSP 详细讲解
1、什么是JSP
Java Server Pages: Java服务器端页面,也和Servlet一样,用于动态Web技术!
最大的特点:
- 写JSP就像在写HTML
- 区别
- 写JSP就像在写HTML
- JSP页面中可以嵌入JAVA代码,为用户提供动态数据
2、JSP原理
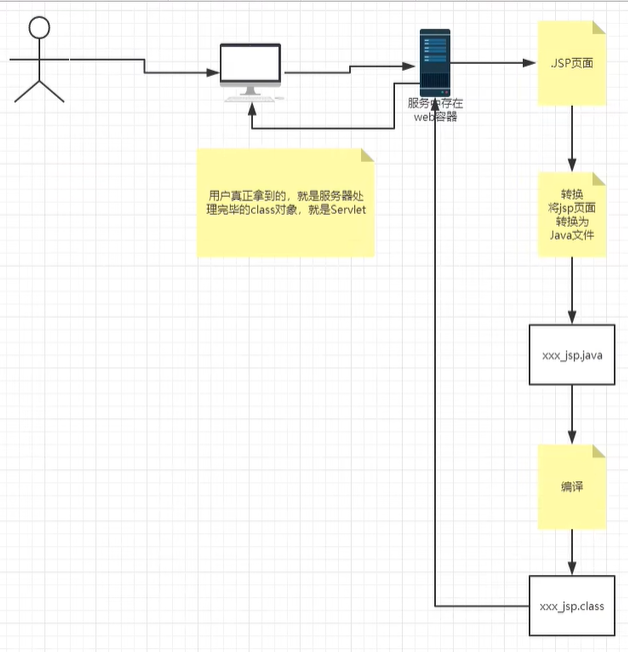
思路:JSP到底是怎么执行的!
-
代码层面没有任何问题
-
服务器内部工作
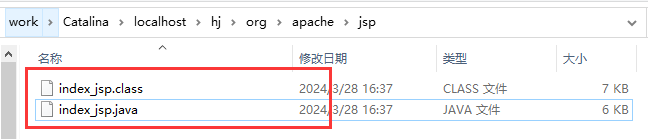
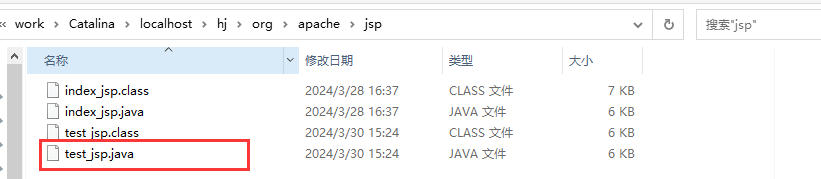
tomcat内部中有一个word目录;
IDEA中使用Tomcat会在IDEA中的tomcat中产生一个work目录

C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\JetBrains\IntelliJIdea2021.2\tomcat\05b63073-44dd-4980-b527-ab3dab02aaed\work\Catalina\localhost\hj\org\apache\jsp
浏览器像服务器放松请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet!
JSP最终也会被转成一个Java类!
Jsp本质上就是一个Servlet


// 初始化
public void _jspInit() {
}
// 销毁
protected void _jspDestroy() {
}
// JSPService
public abstract void _jspService(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2);
内置对象

输出页面前增加的代码

在JSP中访问一个jsp页面才回生成一个_jsp.java文件
访问首页


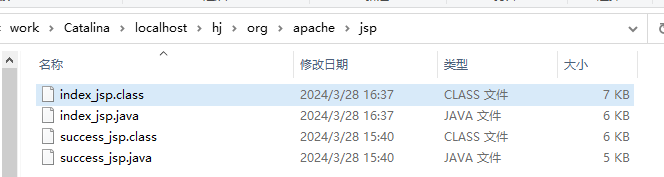
访问多一个就就错一对java文件
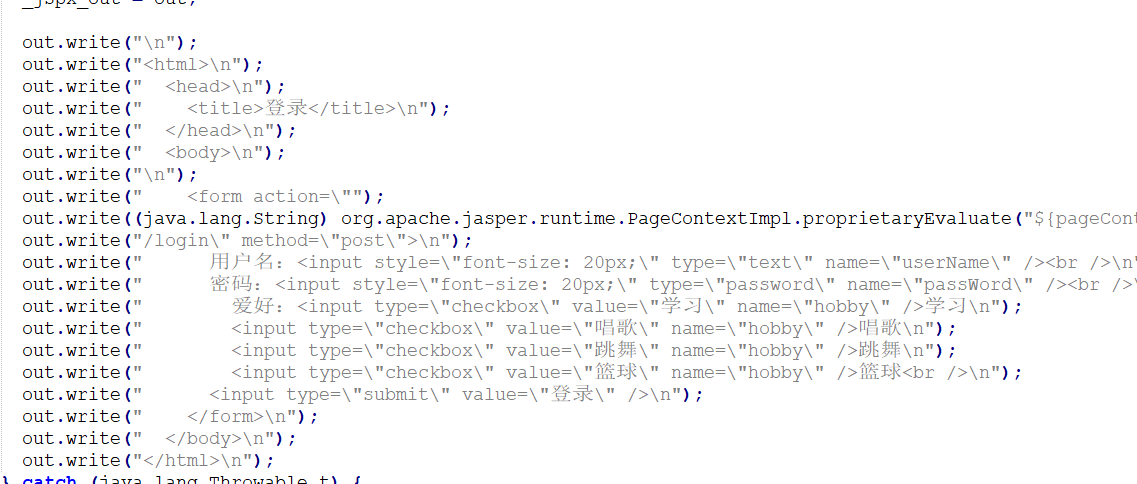
在jsp.java中他实际还是将前端文件转成java类然后通过response输出到前端的
编写一个测试jsp语法的jsp文件
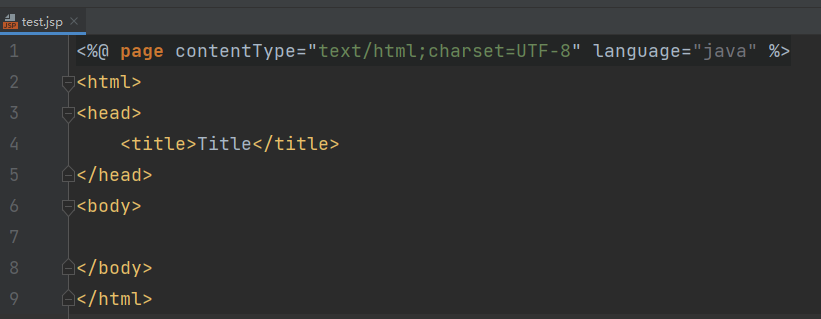
编写代码
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%-- <% 在中间可以写任意java代码 %> --%>
<%
String name = "怀旧";
%>
<%-- 直接输出变量 --%>
<%=name%>
</body>
</html>
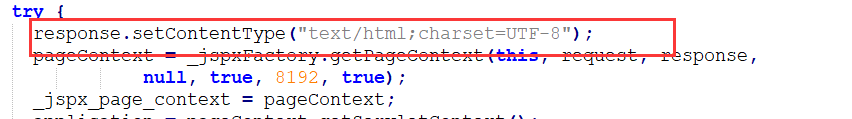
查看运行后的jsp.java文件
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write("<head>\r\n");
out.write(" <title>Title</title>\r\n");
out.write("</head>\r\n");
out.write("<body>\r\n");
<% String name = "怀旧"; %>
String name = "怀旧"; // 直接将前端代码转成java中的代码原封输出<% String name = "怀旧"; %>
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" ");
out.print(name); // <%=name%>
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("</body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>\r\n");
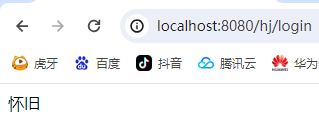
访问结果如上,成功读取到了数据
在JSP页面中:
只要是JAVA代码就会原封不动的输出;
String name = "怀旧";
如果是html代码,就会转为:
out.write("<html>\n");
这样的格式输出到前端1
3、JSP的基础语法

JSP注释:
<%-- jsp中的注释为这样 --%>
JSP表达式:
<%-- JSP表达式
作用: 用来将程序输出,输出到客户端
使用方式 <%= 里面可以写变量或者表达式 %>
相当于调用java中的 out.print( 变量或者表达式 );
--%>
<%= "怀旧" %>
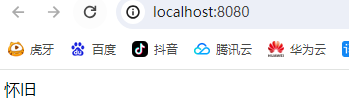
提示jsp的注释在前端源代码不会显示;
<%-- jsp中的注释为这样 --%>
<!-- jsp中的注释为这样 --%>

JSP代码块:
<%-- jsp脚本片段(里面可以编写所有java中可以写的代码) --%>
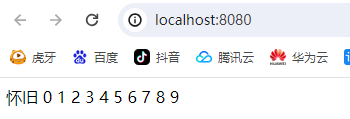
<%
int a = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
out.println(i);
}
%>
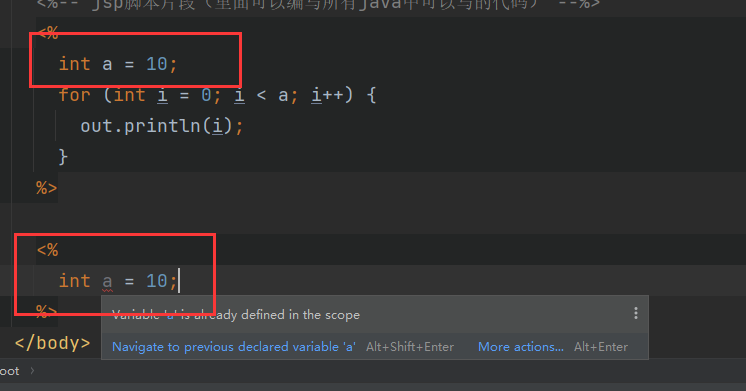
由于在一个界面中会生成一个java文件,并且java文件的内容都在一个方法里:所以不能定义两个同名的变量。
但是这样就可以在不同的代码片段使用同一个变量。
<%
out.println("a的值为:" + a);
%>
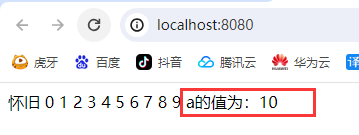
看下面代码:
<%
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
out.println("<h"+i+">"+"我是h"+i+"标签"+"</h\"+i+\">");
}
%>
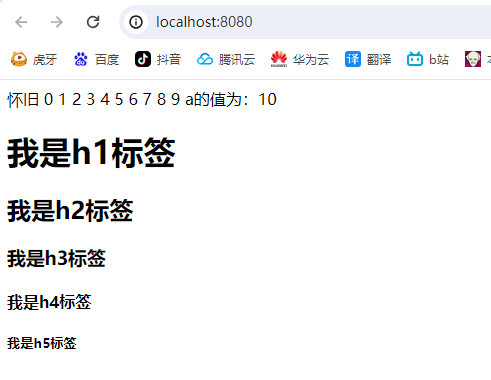
输出结果如下,同样我们可以修改代码写法:
拆分代码块:
<%
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
%>
<h<%=i%>>我是h<%=i%>标签</h<%=i%>>
<%
}
%>
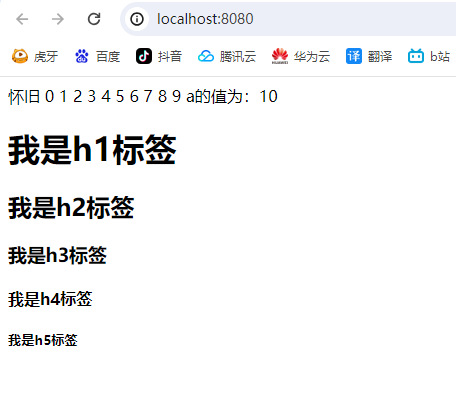
同样输出结果:
让html代码变得灵活起来
查看_jsp.java看看里面将我们代码到底转成了什么样子:
out.write("<html>\n");
out.write(" <head>\n");
out.write(" </head>\n");
out.write(" <body>\n");
out.write(" ");
out.write("\n");
out.write(" ");
out.print( "怀旧" );
out.write("\n");
out.write("\n");
out.write(" ");
out.write("\n");
out.write(" ");
int a = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
out.println(i);
}
out.write("\n");
out.write("\n");
out.write(" ");
out.println("a的值为:" + a);
out.write("\n");
out.write(" <br />\n");
out.write(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
out.write("\n");
out.write(" <h");
out.print(i);
out.write(">我是h");
out.print(i);
out.write("标签</h");
out.print(i);
out.write(">\n");
out.write(" ");
}
out.write("\n");
out.write(" </body>\n");
out.write("</html>\n");
JSP声明的写法:
<%!
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块加载运行...");
}
public static int testNumber = 20;
public static String aa(String str1){
return str1+":怀旧";
}
%>
测试:
<%
out.print(testNumber);
out.print(aa("用户名"));
%>
运行结果查看:

得到运行结果
查看_jsp.java文件
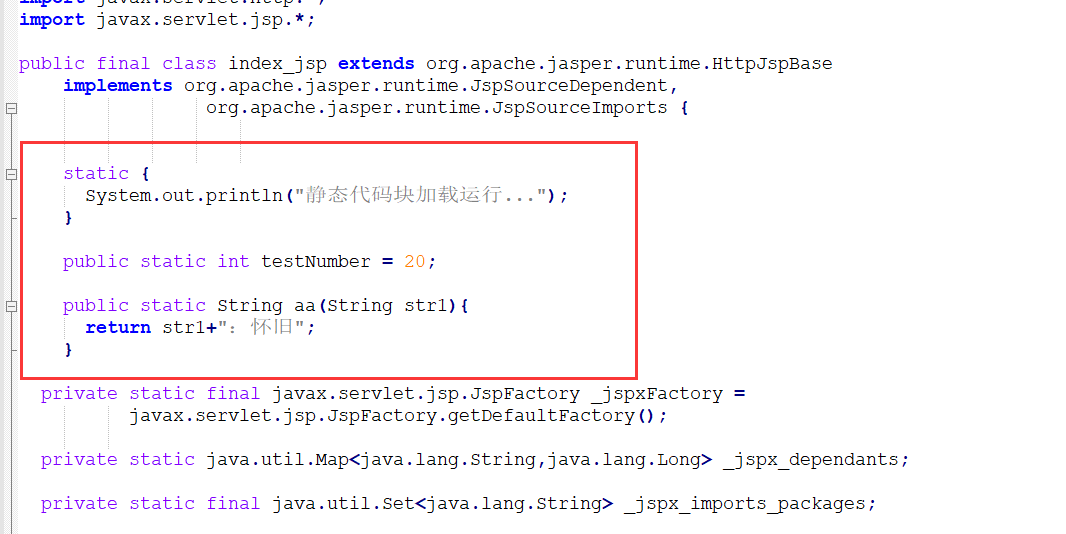
可以看到我们编写在<%! %> 中的代码编写在生成java文件的时候,内容会放在我们的类里面并不是方法里面:
得出结论:
- 在代码块中的代码会被生成在_jspService()方法中
- 而声明的代码会被生成在类里面(可以定义变量和编写方法)
4、JSP中的指令
Jsp包含三个编译指令和七个动作指令。 三个编译指令为:
- page
- include
- taglib。
七个动作指令为:
- jsp:forward
- jsp:param
- jsp:include
- jsp:plugin
- jsp:useBean
- jsp:setProperty
- jsp:getProperty
1、编译指令
1、 page指令
通常位于jsp页面的顶端,同一个页面可以有多个page指令
语法格式如下:
〈% @page
[language="Java"]
[extends="package.class"]
[import= "package. class I package. *},…"]
[session="true I false"]
[buffer="none I 8kb I size kb" 1
[autoFlush="true I false"]
[isThreadSafe="true I false"]
[info="text"]
[errorPage="relativeURL"]
[contentType="mimeType[ ;charset=characterSet]" I"text/html;charset= "808859-1"]
[isErrorPage=" true I false"]
%〉
1.1 language属性
一般情况就是java,代表jsp页面使用的脚本语言。
1.2 Extends属性
确定 JSP 程序编译时所产生的 Java 类,需要继承的父类,或者需要实现的接口的全限定类名。
1.3 import属性
用来导入包,下面几个包是默认自动导入的,不需要显式导入。
默认导入的包有:
java.lang.*
javax.servlet.*
javax.servlet.jsp.*
javax.servlet.http.*
1.4 Session属性
设定这个 JSP 页面是否需要 HTIP session
1.5 buffer属性
指定输出缓冲区的大小。输出缓冲区的 JSP 内部对象: out 用于缓存 JSP页面对客户浏览器的输出,默认值为 8kb,可以设置为 none ,也可以设置为其他值,单位为kb
1.6 autoFlush属性
当输出缓冲区即将溢出时,是否需要强制输出缓冲区的内容。设置为true 时为正常输出;如果设置为 false ,会在 buffer 溢出时产生一个异常。
1.7 Info属性
设置该 JSP 程序的信息,也可以看做其说明,可以通过 Servlet. getServletInfo()方法获取该值。如果在 JSP 页面中,可直接调用 getServletInfoO方法获取该值,因为 JSP 页面的实质就是 Servlet 。 errorPage属性,指定错误处理页面。如果本程序产生了异常或者错误,而该 JSP 页面没有对应的处理代码,则会自动调用该指令所指定的 JSP 页面。使用 JSP 页面时,可以不处理异常,即使是 checked 异常。(重定向到对应的错误处理页面,但是URL还是原来的URl,并不发生变化)如果这个页面不存在这个属性,那么一旦代码出现问题,就会在开发环境和IE浏览器上提示错误。可见这条属性控制异常处理的效果在表现形式上要好的多。
1.8 IsErrorPage属性
设置本 JSP 页面是否为错误处理程序。如果该页面本身己是错误处理页面,则无须使用 errorPage 属性。
1.9 ContentType属性
用于设定生成网页的文件格式和编码方式,即 MIME 类型和页面字符集类型,默认的 MIME 类型是 text/html; 默认的字符集为 ISO-8859-1 。
2、include指令
使用 include 指令,可以将一个外部文件嵌入到当前 JSP 文件中,同时解析这个页面中的 JSP 语句(如果有的话)。这是个静态的 include 语旬,不会检查所包含 JSP 页面的变化。
include 既可以包含静态的文本,也可以包含动态的 JSP 页面。静态的编译指令include ,是将被包含的页面加入进来,生成一个完整的页面。
include 编译指令的语法:
〈% @include file="relativeURLSpec" %〉
如果被嵌入的文件经常需要改变,建议使用jsp:include操作指令,因为它是动态的 include 语句。 包含include指令的jsp页面在部署后,经过访问编译生成java文件,在tomcat的 work\Catalina\localhost\project\org\apache\jsp目录下会生成对应的java文件,这些文件与jsp的名字相同,他包含了编译后的代码,甚至include包含的另外一个jsp的代码也被相应的加入了进来。
2、动作指令
2.1 forward指令
forward 指令用于将页面响应控制转发给另外的页面。既可以转发给静态的 HTML页面,也可以转发到动态的 JSP 页面,或者转发到容器中的 Servlet。
JSP 的 forward 指令的格式如下:
<jsp:forward page=”{relativeURL |<%=expression%>}” />
<jsp:forward page=”{relativeURL |<%=expression%>}”>
{<jsp:param…/>}
</jsp:forward>
第二种语法用于在转发时增加额外的请求参数。增加的请求参数的值可以通过HttpServletRequest 类的 getParameter方法获取。
2.2 include指令
它是一个动态的指令,可以用于导入某个页面。它的导入会每次检查被导入页面的改变。
下面是include指令的使用格式:
<jsp:include page=”{relativeURL |<%=expression%>}” flush=”true” />
<jsp:include page=”{relativeURL |<%=expression%>}” flush=”true”>
<jsp:param name=”paramName” value=”paramValue”/>
</jsp:include>
flush 属性用于指定输出缓存是否转移到被导入文件中。如果指定为剧。则包含在被导入文件中;如果指定为false,则包含在原文件中。对于JSP 1.1以下的旧版本,只能设置为false。 < include >和< jsp:include >分别为静态导入和动态导入。他们的的区别:静态导入是将被导入页面的代码完全插入,两个页面生成一个整体的 Servlet; 而动态导入则在 Servlet 中使用动态导入,从而将页面引入。
2.3 useBean、setProperty和getProperty指令
这三个指令都是与JavaBean相关的指令,其中useBean用于在jsp页面初始化一个java实例,setProperty用于修改JavaBean实例的属性,getProperty用于获取JavaBean实例的属性。 useBean的语法格式:
<jsp:useBean id=”” class=”” scope=”page | request |session | application” >
Id是JavaBean的实例名,class属性确定JavaBean的实现类。Scope属性确定生存范围【页面、请求、会话、应用】 setProperty的语法格式:
<jsp:setProperty name=”” property=”” value=”” />
Name属性确定需要设定
2.4 plugin指令
plugin 指令主要用于下载服务器端的 JavaBean 或 Applet 到客户端执行。由于程序在客户端执行,因此客户端必须安装虚拟机。 plugin 的语法格式如下:
<jsp:plugin type=”bean | applet"
code="classFileName"
codebase="classFileDiretoryName"
[name=" instanceName"]
[archive="URLtoArchive"]
[align= "bottom I top I middle I left I right"]
[heigh="displayPixels"]
[width="displayPixels"]
[hspace="leftRightPixels"]
[vspace="topBottomPiexels"]
[jreversion=JREVersionNumber|1.2"]
[nspluginurl="URLToPlugin"]
[iepluginurl="URLToPlugin"]>
[<jsp:parames>
[jsp:param name="parameterName" value="parameterValue" />]
</jsp:params>]
[<jsp:fallback>text message for user that can no see the plugin
</jsp:fallback> ]
</jsp:plugin>
这些属性的说明如下: Type: 指定被执行的java程序的类型,是一个bean还是一个applet Code: 指定被执行的文件名,该属性值必须以“.class”扩展名结尾 Codebase: 指定被执行的文件目录。 Name: 给该程序起一个名字用来标识该程序。 Archive: 指向一些要预先载入的将要使用到的类的路径。 Hspace,Vspace: 显示左右上下的留白。 jreversion: 能正确运行改程序必须的JRE版本。 Nsplugin,ieplugin: Netscape Navigator, Internet Exploer 下载运行所需JRE 的地址。 < jsp:fallback >指令:当不能正确显示该applet时,代替显示的提示信息。
2.5 param指令
param指令用于设置参数值,这个指令本身不能单独使用,因为单独使用没有意义。它可以和以下几个指令合起来使用 jsp:include jsp:forward jsp:plugin
5、JSP中的9大内置对象
- PageContext 存东西
- Requset 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application 【ServletContext】 存东西
- config 【ServletConfig】
- out
- page
- exception
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("userName1", "怀旧1");
request.setAttribute("userName2", "怀旧2");
session.setAttribute("userName3", "怀旧3");
application.setAttribute("userName4", "怀旧4");
%>
<%
String userName1 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName1");
String userName2 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName2");
String userName3 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName3");
String userName4 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName4");
// 获取一个不存在的值
String userName5 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName5");
%>
<%--使用EL表达式获取输入的值--%>
<h4>${userName1}</h4>
<h4>${userName2}</h4>
<h4>${userName3}</h4>
<h4>${userName4}</h4>
<h4>${userName5}</h4>
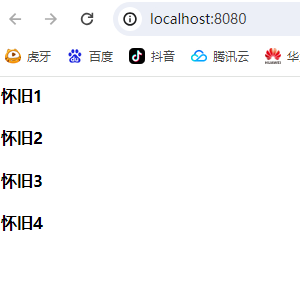
使用了EL表达式可以看到userName5没有输出,换为<%=%>测试
<h4><%=userName5%></h4>
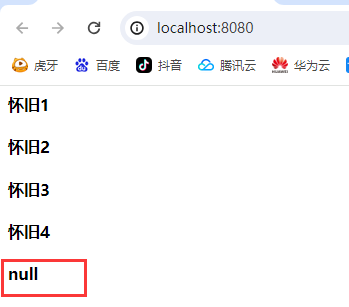
测试其他界面访问数据:
创建一个新的jsp界面
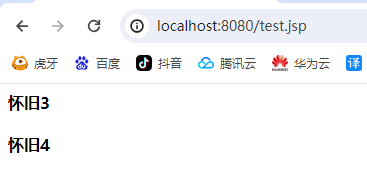
访问到了session的和application的数据,page(当前界面) request(当前请求的)都无法访问到。
测试通过转发看能够访问到request的数据:
<%
String userName1 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName1");
String userName2 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName2");
String userName3 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName3");
String userName4 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName4");
// 获取一个不存在的值
String userName5 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("userName5");
pageContext.forward("/test.jsp");
%>
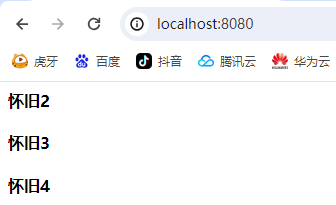
成功获取到request的数据.
6、JSP标签、JSTL、EL标签
EL表达式: ${ }
- 获取数据
- 执行运算
- 获取web开发的常用对象
JSP标签使用测试:
首先需要导入需要的包:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.web</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-impl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
测试使用jsp标签实现界面跳转:
创建jsp1.jsp文件
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>界面1</h1>
<%-- 通过forward来进行页面跳转,跳转的同时传入参数 --%>
<jsp:forward page="jsp2.jsp">
<jsp:param name="name" value="huaijiu"/>
<jsp:param name="password" value="123456"/>
</jsp:forward>
</body>
</html>
jsp2.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>界面2</h1>
<br />
<%-- 获取参数并输出 --%>
用户名:<%=request.getParameter("name")%><br/>
密码:<%=request.getParameter("password")%>
</body>
</html>
测试访问jsp1界面
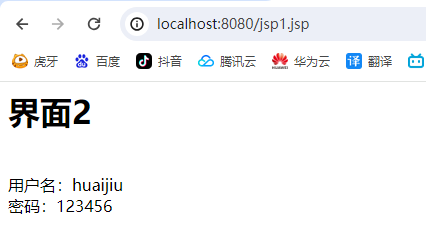
输出结果为界面2,并且同时将数据成功转到界面2
JSTL表达式
参考链接:网页链接






评论
登录后才可以进行评论哦!